The Autonomous Shopping-Guide Robot in Cashier-Less Convenience Stores
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46604/peti.2020.3961Keywords:
ROS (Robot Operating System), wireless networks, navigation, autonomous driving, cashier-less convenience store, route planning, genetic algorithmAbstract
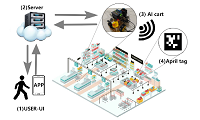
In recent years, several cashier-less convenience stores have appeared, including Amazon’s. A store without cashiers will become a trend in the near future. To substitute the employee in traditional stores, this research proposes and designs an autonomous shopping cart robot to guide customers’ purchase according to the requested shopping list to enhance their shopping experience. The core techniques of the system are the autonomous driving robot, the traffic control center for robots and the dynamic route planning algorithm. The robot is a self-propelled vehicle developed by ROS (Robot Operating System), in which we achieve the automatic driving via image recognition, April tag identification and driving direction guidance from the path planning and traffic control services. This enables the robot to lead customers to find their commodities following the preplanned route. In conjunction with the vocal service, the robot can notify the customer when arriving at each commodity, he or she plans to buy. We also design a light APP for customers to easily set up and manage their shopping list, call for the robotic shopping cart’s help, and interact with the shopping cart robot. To enhance the shopping experience of customers, we design the dynamic route planning genetic algorithm to dynamically plan the shopping route according to the customer’s request and the traffic condition. Experiments show that our genetic algorithm can provide the most stable performance and always get efficient shopping route planning in a limited time compared to other methods.
References
What is Duckietown? Online Available: http://duckietown.mit.edu/
L. Paull, J. Tani, H. Ahn, et al, “Duckietown: an open, inexpensive and flexible and capable platform for autonomy education and research,” 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2017, pp. 1497-1504.
J. Tani, L. Paull, M. T. Zuber, D. Rus, J. How, J. Leonard, and A. Censi, “Duckietown: an innovative way to teach autonomy,” International Conference EduRobotics 2016, 2016, pp. 104-121.
Chi-Shian Lin, “Study on map-based indoor mobile robot vision navigation,” Matster’s Thesis of Department of Electrical Engineering, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan, 2009.
Ö. Ş. Taş, F. Kuhnt, J. M. Zöllner, and C. Stiller, “Functional system architectures towards fully automated driving,” 2016 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), June 2016, pp.304-309.
A. Hellmund, S.Wirges, Ö. Ş. Taş, C. Bandera, and N. O. Salscheider “Robot operating system: a modular software framework for automated driving,” 2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), 2016.
Inside Amazon Go, a Store of the Future Online Available: https://www.nytimes.com/2018/01/21/technology/inside-amazon-go-a-store-of-the-future.html
D. Grewal, A. L. Roggeveen, and J. Nordfält, “The future of retailing,” Journal of Retailing, vol. 93, no. 1, pp. 1-6, 2017.
M. R. Garey and D. S. Johnson, “Computers and intractability: a guide to the theory of NP-completeness,” W. H. Freeman and Company, San Francisco, 1979.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Submission of a manuscript implies: that the work described has not been published before that it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere; that if and when the manuscript is accepted for publication. Authors can retain copyright of their article with no restrictions. Also, author can post the final, peer-reviewed manuscript version (postprint) to any repository or website.

Since Oct. 01, 2015, PETI will publish new articles with Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, under The Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) License.
The Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial (CC-BY-NC) License permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes







