Remote Monitoring for the Operation Status of CNC Machine Tools Based on HTML5
Keywords:
CNC machine tool, remote monitoring, HTML5, 3D modelAbstract
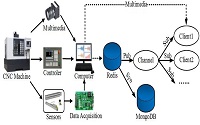
In order to improve the accuracy of remote monitoring of computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools and reduce the difficulty of monitoring; a remote monitoring method for CNC machine tools based on HTML5 is proposed in this paper. The core idea of this method is to record external sensor information and internal working condition information in the same time, and then visualize the information in multiple directions. Monitoring accuracy is improved through the combined use of internal and external information. In response to the difficult problem of traditional method monitoring; the internal working condition information, external sensor information, 3D model and multimedia information of CNC machine tools are jointly visualized. The 3D model synchronous motion is driven by real-time working condition data. Remote low-latency multimedia information transmission is implemented by using cloud live broadcast technology.
References
Y. Cai, B. Starly, P. Cohen, and Y. S. Lee, “Sensor data and information fusion to construct digital-twins virtual machine tools for cyber-physical manufacturing,” Procedia Manufacturing, vol. 10, pp. 1031-1042, 2017.
X. H. Li and W. Y. Li, “The research on intelligent monitoring technology of NC machining process,” Procedia CIRP, vol. 56, pp. 556-560, 2016.
E. Y. Heo, H. Lee, C. S. Lee, D. W. Kim, and D. Y. Lee, “Process monitoring technology based on virtual machining,” Procedia Manufacturing, vol. 11, pp. 982-988, 2017.
Z. Lei, W. Hu, and H. Zhou, “Deploying web-based control laboratory using HTML5,” 2016 13th International Conference on Remote Engineering and Virtual Instrumentation (REV), Madrid, pp. 69-73, 2016.
Y. Sheng, J. Huang, F. Zhang, Y. An, and P. Zhong, “A virtual laboratory based on HTML5,” 2016 11th International Conference on Computer Science & Education (ICCSE), Nagoya, pp. 299-302, 2016.
J. Chen, J. Yang, H. Zhou, H. Xiang, Z. Zhu, Y. Li, C. H. Lee, and G. Xu, “CPS modeling of CNC Machine Tool work processes using an instruction-domain based approach,” Engineering, vol. 1, pp. 247-260, 2015.
J. Y. Xia, B. J. Xiao, D. Li, and K. R. Wang, “Interactive WebGL-based 3D visualizations for EAST experiment,” Fusion Engineering and Design, vol. 112, pp. 946-951, 2016.
L. Lianzhong, Z. Kun, and X. Yang, “A Cloud-Based framework for robot simulation using WebGL,” 2015 Sixth International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Engineering Applications (ISDEA), Guiyang, pp. 5-8, 2015.
A. S. Rosas and J. L. A. Martínez, “Videoconference system based on WebRTC with access to the PSTN,” Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science, vol. 329, pp. 105-121, 2016.
Sredojev, D. Samardzija, and D. Posarac, “WebRTC technology overview and signaling solution design and implementation,” in 2015 38th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), 25-29 May 2015, Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015.
K. I. Z. Apu, N. Mahmud, F. Hasan, and S. H. Sagar, “P2P video conferencing system based on WebRTC,” 2017 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE), Cox's Bazar, pp. 557-561, 2017.
S. Dumke, H. Riemann, T. Bluhm, R. Daher, M. Grahl, M. Grün, A. Holtz, J. Krom, G. Kühner, H. Laqua, M. Lewerentz, A. Spring, and A. Werner, “Next generation web based live data monitoring for W7-X,” Fusion Engineering and Design, vol. 129, pp. 16-23, 2018.
Z. Yongliang and L. Zhiyuan, “Stability and online monitoring of cutting chatter: a review,” Applied Mechanics and Materials, vol. 121-126, pp. 377-81, 2011.
K. J. Li, Y. X. Liu, and Z. Zhao, “Research in multiple factors vibration controlling of CNC milling machine,” 2011 Fourth International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, Shenzhen, Guangdong, pp. 472-475, 2011.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Submission of a manuscript implies: that the work described has not been published before that it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere; that if and when the manuscript is accepted for publication. Authors can retain copyright in their articles with no restrictions. is accepted for publication. Authors can retain copyright of their article with no restrictions.
Since Jan. 01, 2019, AITI will publish new articles with Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, under The Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) License.
The Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial (CC-BY-NC) License permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.



