The Study of the Microbes Degraded Polystyrene
Keywords:
polystyrene, tenebrio molitor, zophobas morio, 16S rDNA sequencingAbstract
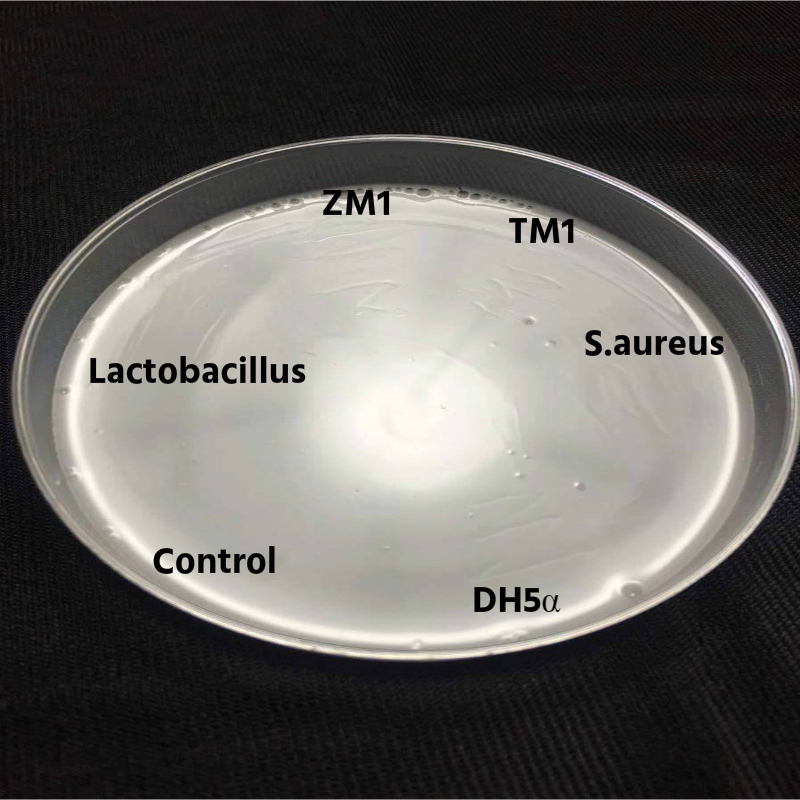
Under the observation that Tenebrio molitor and Zophobas morio could eat polystyrene (PS), we setup the platform to screen the gut microbes of these two worms. To take advantage of that Tenebrio molitor and Zophobas morio can eat and digest polystyrene as its diet, we analyzed these special microbes with PS plate and PS turbidity system with time courses. There were two strains TM1 and ZM1 which isolated from Tenebrio molitor and Zophobas morio, and were identified by 16S rDNA sequencing. The results showed that TM1 and ZM1 were cocci-like and short rod shape Gram-negative bacteria under microscope. The PS plate and turbidity assay showed that TM1 and ZM1 could utilize polystyrene as their carbon sources. The further study of PS degraded enzyme and cloning warrants our attention that this platform will be an excellent tools to explore and solve this problem.References
K. Desmet, M. Schelfaut, and P. Sandra, “Determination of bromophenols as dioxin precursors in combustion gases of fire retarded extruded polystyrene by sorptive sampling-capillary gas chromatography–mass spectrometry,” Journal of Chromato-graphy A, vol. 1071, pp. 125-129, April 4, 2005.
H. Nishizaki, K. Yoshida, and J. Wang, “Comparative study of various methods for thermogravimetric analysis of polystyrene degradation,” Journal of Applied Polymer Science, vol. 25, pp. 2869-2877, 1980.
D. Kaplan, R. Hartenstein, and J. Sutter, “Biodegradation of polystyrene, poly (metnyl methacrylate), and phenol formaldehyde,” Applied and environmental microbiology, vol. 38, pp. 551-553, 1979.
Y. Yang, J. Yang, W. M. Wu, J. Zhao, Y. Song, L. Gao, R. Yang, and L. Jiang, “Biodegradation and mineralization of polystyrene by plastic-eating mealworms: part 1. chemical and physical characteriza- tion and isotopic tests,” Environmental science & technology, vol. 49, pp. 12080- 12086, 2015.
J. Yang, Y. Yang, W. M. Wu, J. Zhao, Y. Song, L. Gao, R. Yang, and L. Jang, “Biodegradation and mineralization of polystyrene by plastic-eating mealworms. 2. role of gut microorganisms (Supporting information),” Environmental science and Technology, vol. 49, no. 20, October, 2015.
T. K. Chua, M. Tseng, and M. K. Yang, “Degradation of poly (ε-caprolactone) by thermophilic streptomyces thermo- violaceussubsp. thermoviolaceus 76T-2,” AMB Express, vol. 3, p. 8, 2013.
B. van den Bogert, W. M. de Vos, E. G. Zoetendal, and M. Kleerebezem,“Microarray analysis and barcoded pyrosequencing provide consistent microbial profiles depending on the source of human intestinal samples,” Applied and environmental microbiology, vol. 77, pp. 2071-2080, 2011.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Submission of a manuscript implies: that the work described has not been published before that it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere; that if and when the manuscript is accepted for publication. Authors can retain copyright in their articles with no restrictions. is accepted for publication. Authors can retain copyright of their article with no restrictions.
Since Jan. 01, 2019, AITI will publish new articles with Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, under The Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) License.
The Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial (CC-BY-NC) License permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.



