Real Time Scanning-Modeling System for Architecture Design and Construction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.46604/aiti.2020.5385Keywords:
scanning-modeling system, material data, computational design, robotic constructionAbstract
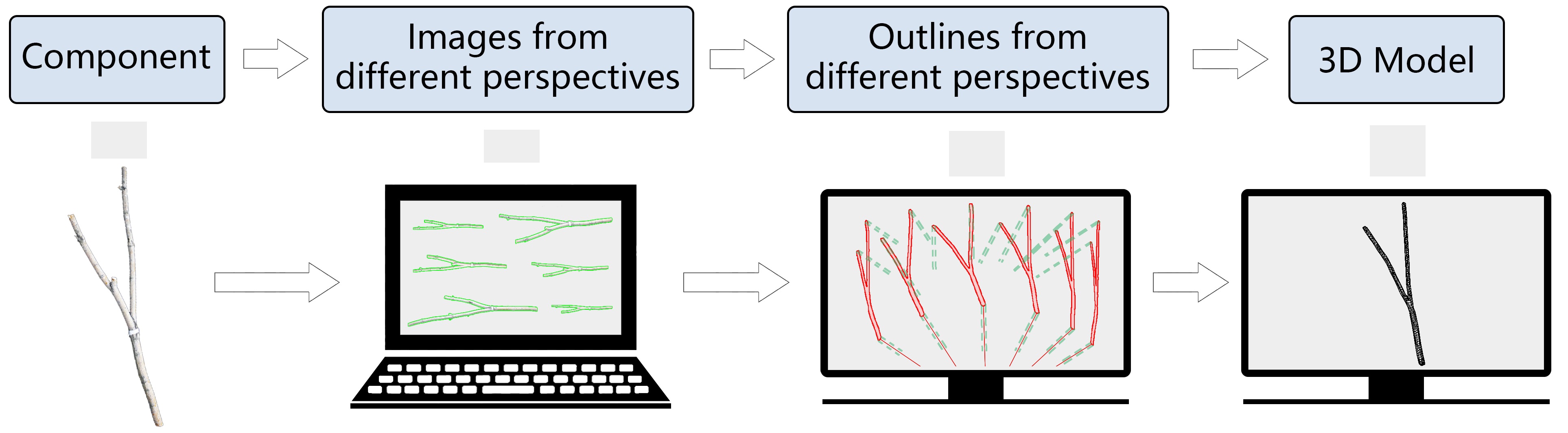
The disconnection between architectural form and materiality has become an important issue in recent years. Architectural form is mainly decided by the designer, while material data is often treated as an afterthought which doesn’t factor in decision-making directly. This study proposes a new, real-time scanning-modeling system for computational design and autonomous robotic construction. By using cameras to scan the raw materials, this system would get related data and build 3D models in real time. These data would be used by a computer to calculate rational outcomes and help a robot make decisions about its construction paths and methods. The result of an application pavilion shows that data of raw materials, architectural design, and robotic construction can be integrated into a digital chain. The method and gain of the material-oriented design approach are discussed and future research on using different source materials is laid out.
References
K. Wu and A. Kilian, “Design natural wood log structures with stochastic assembly and deep learning,” Robotic fabrication in architecture, art and design, Springer Press, August 2018, pp. 16-30.
A. Picon, Architecture and the virtual: towards a new materiality, Wissenschaftliche Zeitschrift der Bauhaus-Universität Weimar, 2003.
N. Leach, “Digital cities,” Architectural Design, vol. 79, no. 4, pp. 6-13, June 2009.
F. Gramazio, M. Kohler, and J. WillMann, The robotic touch: How robots change architecture: Gramazio&Kohler Research ETH Zurich 2005-2013, 1st ed. Zurich: Park Books, 2014.
F. Chen, G. M. Brown, and M. Song, “Overview of 3-D shape measurement using optical methods,” Optical Engineering, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 10-22, January 2000.
R. Zhu, O. Furxhi, D. Marks, and D. Brady, “Millimeter wave surface and reflectivity estimation based on sparse time of flight measurements,” 39th International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz waves (IRMMW-THz), IEEE Press, September 2014, pp. 1-2.
J. Schlarp, E. Csencsics, and G. Schitter, “Scanning laser triangulation sensor geometry maintaining imaging condition,” IFAC-Papers Online, vol. 52, no. 15, pp. 301-306, December 2019.
M. Slembrouck, P. Veelaert, D. Hamme, D. Van Cauwelaert, and W.Philips, “Cell-Based Approach for 3D Reconstruction from Incomplete Silhouettes,” International Conference on Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems, Springer Press, September 2017, pp. 530-541.
J. S. Franco and E. Boyeb, “Efficient polyhedral modeling from silhouettes,” IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, April 2009, pp. 414-427.
H. Hua, “A bi-directional procedural model for architectural design,” Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 36, no. 8, pp. 219-231, December 2017.
G. Brugnaro, E. Baharlou, L. Vasey, and A. Menges, “Robotic softness-an adaptive robotic fabrication process for woven structures,” Proc. 36th Annual Conference of the Association for Computer Aided Design in Architecture, October 2016, pp. 154-163.
P. Eversmann, F. Gramazio, and M. Kohler, “Robotic prefabrication of timber structures: towards automated large-scale spatial assembly,” Construction Robotics, vol. 1, no. 1-4, pp. 49-60, August 2017.
M. Maasoumy and A. Sangiovanni-Vincentelli, “Smart connected buildings design automation: foundations and trends,” Foundation and Trends in Electronic Design Automation, vol. 10, no. 1-2, pp. 1-143, March 2016.
R. Snooks and G. Jahn, “Closeness: on the relationship of multi-agent algorithms and robotic fabrication,” Robotic fabrication in architecture, art and design, Springer Press, February 2016, pp. 218-229.
J. P. Sousa, C. G. Palop, E. Moreira, A. M. Pinto, J. Lima, P. Costa, et al. “The SPIDERobot: a cable-robot system for on-site construction in architecture,” Robotic Fabrication in Architecture, Art and Design, Springer Press, February 2016, pp. 230-239.
R. Rust, D. Jenny, F. Gramazio, and M. Kohler, “Spatial wire cutting: cooperative robotic cutting of non-ruled surface geometries for bespoke building components,” Proc. 21st International Conference on Computer-Aided Architectural Design Research in Asia, Southeastern University Press, March-April 2016, pp. 529-538.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Submission of a manuscript implies: that the work described has not been published before that it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere; that if and when the manuscript is accepted for publication. Authors can retain copyright in their articles with no restrictions. is accepted for publication. Authors can retain copyright of their article with no restrictions.
Since Jan. 01, 2019, AITI will publish new articles with Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, under The Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) License.
The Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial (CC-BY-NC) License permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.







