Prediction of Pressure Gradient in Two and Three-phase Flows in Horizontal Pipes Using an Artificial Neural Network Model
Keywords:
Artificial neural networks, two-phase flow, three-phase flow, pressure drop, horizontal pipesAbstract
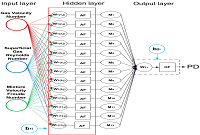
Concurrent flow of gas with a mixture of oil and water in production equipment is common necessitating the need for additional investigations to gain more insight and development of more accurate correlations for prediction of flow characteristics including pressure drop. In this study, an experimental study was conducted using air-water and air-water-oil mixtures in a 0.075-m diameter pipe. Superficial gas and liquid velocities ranged from 0.03 to 0.13 m/s and 1.26 to 41.58 m/s respectively. Slug flow was the main flow pattern observed. In addition, transition to annular and annular flow were also observed. Due to the homogeneous nature of the oil-water-air mixture, the three-phase flow was evaluated as a pseudo-two-phase mixture. An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model developed for the prediction of two- and three- phase pressure drop performed better than all models considered during the evaluation. Generally, it is found that the accuracies for pressure drop were considered adequate.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright Notice
Submission of a manuscript implies: that the work described has not been published before that it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere; that if and when the manuscript is accepted for publication. Authors can retain copyright in their articles with no restrictions. Also, author can post the final, peer-reviewed manuscript version (postprint) to any repository or website.

Since Jan. 01, 2019, IJETI will publish new articles with Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) License.
The Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial (CC-BY-NC) License permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.



.jpg)


