Design and Evaluation of a Novel Low Acoustic Impedance-Based PZT Transducer for Detecting the Near-Surface Defects
Keywords:
non-destructive testing, low acoustic impedance, self-sensing transducerAbstract
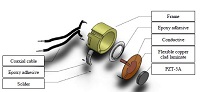
Near-surface defects are one of the most common types of damage occurring in polymer composite materials. Conventional Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) techniques, especially ultrasonic testing, are not always suitable for detecting these types of defect, especially in thin plates. The proposed NDT method in this article employs Low Acoustic Impedance (LAI) characterization. The novelty of LAI technique lies in the transverse resonating of Lead-Zirconate-Titanate (PZT) transducer which shows significant lower effective acoustic impedance compared to thickness - extension mode. The LAI technique eliminates the need for the matching layers and reduces the manufacturing cost consequently. Briefly, the analytical model has been introduced and the fabrication procedure has been discussed in detail. The setup has been evaluated both numerically and experimentally to detect a debonding. The results proved the ability of LAI technique in the detection of defects and, moreover, the approximate geometry of the affected region as well.
References
C. R. Farrar and K. Worden, “An introduction to structural health monitoring,” Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society a-Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences, Editorial Material vol. 365, no. 1851, pp. 303-315, February 2007.
C. R. Farrar and N. A. J. Lieven, “Damage prognosis: the future of structural health monitoring,” Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society a-Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences, Article vol. 365, no. 1851, pp. 623-632, February 2007.
H. Salehi and R. Burgueno, “Emerging artificial intelligence methods in structural engineering,” Engineering Structures, Review vol. 171, pp. 170-189, September 2018.
S. Sony, S. Laventure, and A. Sadhu, “A literature review of next-generation smart sensing technology in structural health monitoring,” Structural Control & Health Monitoring, Review vol. 26, no. 3, p. 22, March 2019.
S. Nezami, S. Lee, K. Kang, and J. Kim, “Improving durability of a vibration energy harvester using structural design optimization,” no. 50497, p. V002T07A018, September 2016.
S. Nezami, H. Jung, M. K. Sung, and S. Lee, “Dynamics of vibration energy harvester governed by gravity and magnetic force in a rotating wind turbine blade,” no. 51951, p. V002T07A002, September 2018.
B. S. Divsholi and Y. W. Yang, “Combined embedded and surface-bonded piezoelectric transducers for monitoring of concrete structures,” Ndt & E International, Article vol. 65, pp. 28-34, July 2014.
W. S. Na and J. Baek, “A review of the piezoelectric electromechanical impedance based structural health monitoring technique for engineering structures,” Sensors, Review vol. 18, no. 5, p. 18, May 2018.
F. G. Baptista, J. Vieira, and D. J. Inman, “Sizing PZT transducers in impedance-based structural health monitoring,” Ieee Sensors Journal, Article vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 1405-1414, June 2011.
K. S. Tan, N. Guo, B. S. Wong, and C. G. Tui, “Comparison of lamb waves and pulse echo in detection of near-surface defects in laminate plates,” NDT & E International, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 215-223, August 1995.
E. La Malfa Ribolla, M. R. Hajidehi, P. Rizzo, G. F. Scimemi, A. Spada, and G. Giambanco, “Ultrasonic inspection for the detection of debonding in CFRP-reinforced concrete,” Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, Article vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 807-816, 2018.
R. Dugnani, “Novel nondestructive evaluation transducer for imaging of low-impedance targets,” Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, Article vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 340-351, February 2015.
D. M. Ai, H. P. Zhu, H. Luo, and C. Wang, “Mechanical impedance based embedded piezoelectric transducer for reinforced concrete structural impact damage detection: A comparative study,” Construction and Building Materials, Article vol. 165, pp. 472-483, March 2018.
A. Narayanan, A. Kocherla, and K. V. L. Subramaniam, “Embedded PZT sensor for monitoring mechanical impedance of hydrating cementitious materials,” Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation, Article vol. 36, no. 4, p. 13, December 2017.
H. A. Tinoco, L. Robledo-Callejas, D. J. Marulanda, and A. L. Serpa, “Damage detection in plates using the electromechanical impedance technique based on decoupled measurements of piezoelectric transducers,” Journal of Sound and Vibration, Article vol. 384, pp. 146-162, December 2016.
R. Dugnani, “Novel transducer for characterization of low-impedance materials,” presented at the Proceedings 4th Asia-Pacific Workshop on SHM, December, 2012.
Elcometer, “http://www.elcometerusa.com/ultrasonic-ndt/Flaw-Detectors,” ed, 2019.
S. Kim et al., “Health monitoring of civil infrastructures using wireless sensor networks,” presented at the Proceedings of the 6th international conference on Information processing in sensor networks, Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, 2007.
P. Gyuhae, S. Hoon, C. R. Farrar, and D. J. Inman, “Overview of piezoelectric impedance-based health monitoring and path forward,” Shock and Vibration Digest, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 451-463, 2003.
R. Dugnani and F. K. Chang, “In vitro atherosclerotic plaque characterization by acoustic impedance monitoring, Part II: Experimentation and validation,” Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, Article vol. 19, no. 7, pp. 827-835, July 2008.
A. Mohammadabadi and R. Dugnani, “Wood defect detection using low acoustic impedance-based PZT transducers,” engrXiv, 2019.
N. Kim, K. Jang, and Y. K. An, “Self-sensing nonlinear ultrasonic fatigue crack detection under temperature variation,” Sensors, Article vol. 18, no. 8, p. 15, August 2018.
A. Mohammadabadi and R. Dugnani, “Damage detection in composites by LAI-PZT transducer,” engrXiv, 2019.
K. Oshima, T. Takigami, and Y. Hayakawa, “Robust vibration control of a cantilever beam using self-sensing actuator,” JSME International Journal, Series C (Mechanical Systems, Machine Elements and Manufacturing), vol. 40, no. 4, pp. 681-687, 1997.
M. Rakotondrabe, I. A. Ivan, S. Khadraoui, P. Lutz, and N. Chaillet, “Simultaneous displacement/force self-sensing in piezoelectric actuators and applications to robust control,” IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 519-531, 2015.
R. Dugnani and F. K. Chang, “In vitro atherosclerotic plaque characterization by acoustic impedance monitoring, Part I: Sensor modeling, design, and fabrication,” Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, Article vol. 19, no. 7, pp. 815-826, July 2008.
R. Dugnani, “Dynamic behavior of structure-mounted disk-shape piezoelectric sensors including the adhesive layer,” Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, Article vol. 20, no. 13, pp. 1553-1564, September 2009.
C. Liang, F. P. Sun, and C. A. Rogers, “Coupled electro-mechanical analysis of adaptive material systems-determination of the actuator power consumption and system energy transfer,” Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 12-20, January 1994.
L. Chen, S. Fanping, and C. A. Rogers, “Electro-mechanical impedance modeling of active material systems,” Smart Materials and Structures, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 171-186, April 1996.
J. Shen and S. Mousavi, “Least sparsity of $p$-norm based optimization problems with $p>1$,” SIAM Journal on Optimization, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 2721-2751, 2018.
V. Gupta, M. Sharma, and N. Thakur, “Optimization criteria for optimal placement of piezoelectric sensors and actuators on a smart structure: A technical review,” Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, Review vol. 21, no. 12, pp. 1227-1243, August 2010.
N. Pérez, F. Buiochi, M. A. Brizzotti Andrade, and J. C. Adamowski, “Numerical characterization of piezoceramics using resonance curves,” Materials (Basel, Switzerland), vol. 9, no. 2, p. 71, 2016.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright Notice
Submission of a manuscript implies: that the work described has not been published before that it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere; that if and when the manuscript is accepted for publication. Authors can retain copyright in their articles with no restrictions. Also, author can post the final, peer-reviewed manuscript version (postprint) to any repository or website.

Since Jan. 01, 2019, IJETI will publish new articles with Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, under Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) License.
The Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial (CC-BY-NC) License permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.



.jpg)


