Reduction of Residual Stresses in Sapphire Cover Glass Induced by Mechanical Polishing and Laser Chamfering Through Etching
Keywords:
picosecond laser, laser curvature method, residual stress, stress relief, wet etching, sapphireAbstract
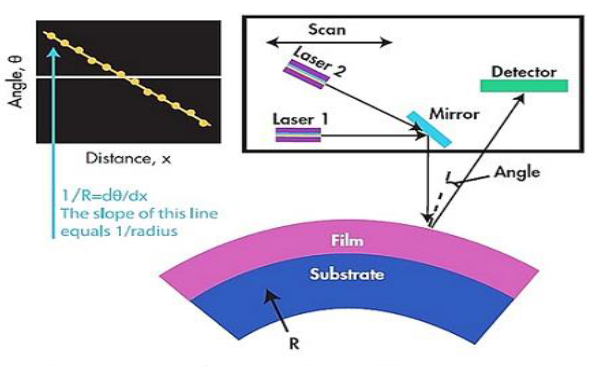
Sapphire is a hard and anti-scratch material commonly used as cover glass of mobile devices such as watches and mobile phones. A mechanical polishing using diamond slurry is usually necessary to create mirror surface. Additional chamfering at the edge is sometimes needed by mechanical grinding. These processes induce residual stresses and the mechanical strength of the sapphire work piece is impaired. In this study wet etching by phosphate acid process is applied to relief the induced stress in a 1” diameter sapphire cover glass. The sapphire is polished before the edge is chamfered by a picosecond laser. Residual stresses are measured by laser curvature method at different stages of machining. The results show that the wet etching process effectively relief the stress and the laser machining does not incur serious residual stress.References
“Gorilla Glass Success, What is Sapphire glass?” http://www.corning.com/news_center/features/gorillaglasssuccess.aspx, Corning Incorporated.
“Everything You Wanted To Know About Sapphire Glass, But Were Afraid To Ask, ” http://www.cultofmac.com/267068/everything-wanted-know-sapphire-glass-afraid-ask-qa/
D. Wang, J. Lee, K. Holland, T. Bibby, S. Beaudoin, and T. Cale, “Von mises stress in chemical‐mechanical polishing processes,” J. Electrochem. Soc., vol. 144, no. 3, pp. 1121-1127, 1997.
G. Kermouche, J. Rech, H. Hamdi, and J. M. Bergheau, “On the residual stress field induced by a scratching round abrasive grain,” Wear, vol. 269, no. 1-2, pp. 86-92, May 2010.
C. Landesberger, C. Paschke, and K. Bock, “Influence of wafer grinding and etching techniques on the fracture strength of thin silicon substrates,” Advanced Materials Research, vol. 325, pp. 659-665, 2011.
K. Gurnett and T. Adams, “Ultra-thin semiconductor wafer applications and processes,” III-Vs Review, vol. 19, pp. 38–40, 2006.
Z. J. Pei, G. R. Fisher, and J. Liu, “Grinding of silicon wafers: a review from historical perspectives,” International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, vol. 48, pp. 1297-1307, 2008.
J. Wang, P. Shrotriya, and K. S. Kim, “Surface residual stress measurement using curvature interferometry,” Experimental Mechanics, vol. 46, pp. 39-46, 2006.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Submission of a manuscript implies: that the work described has not been published before that it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere; that if and when the manuscript is accepted for publication. Authors can retain copyright in their articles with no restrictions. is accepted for publication. Authors can retain copyright of their article with no restrictions.
Since Jan. 01, 2019, AITI will publish new articles with Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, under The Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) License.
The Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial (CC-BY-NC) License permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited and is not used for commercial purposes.



